Kettlebell Lunge: Video Tutorial & Exercise Guide

Written By: Ether Brown
Updated: Oct 13, 2024
| Workout | Kettlebell Lunge |
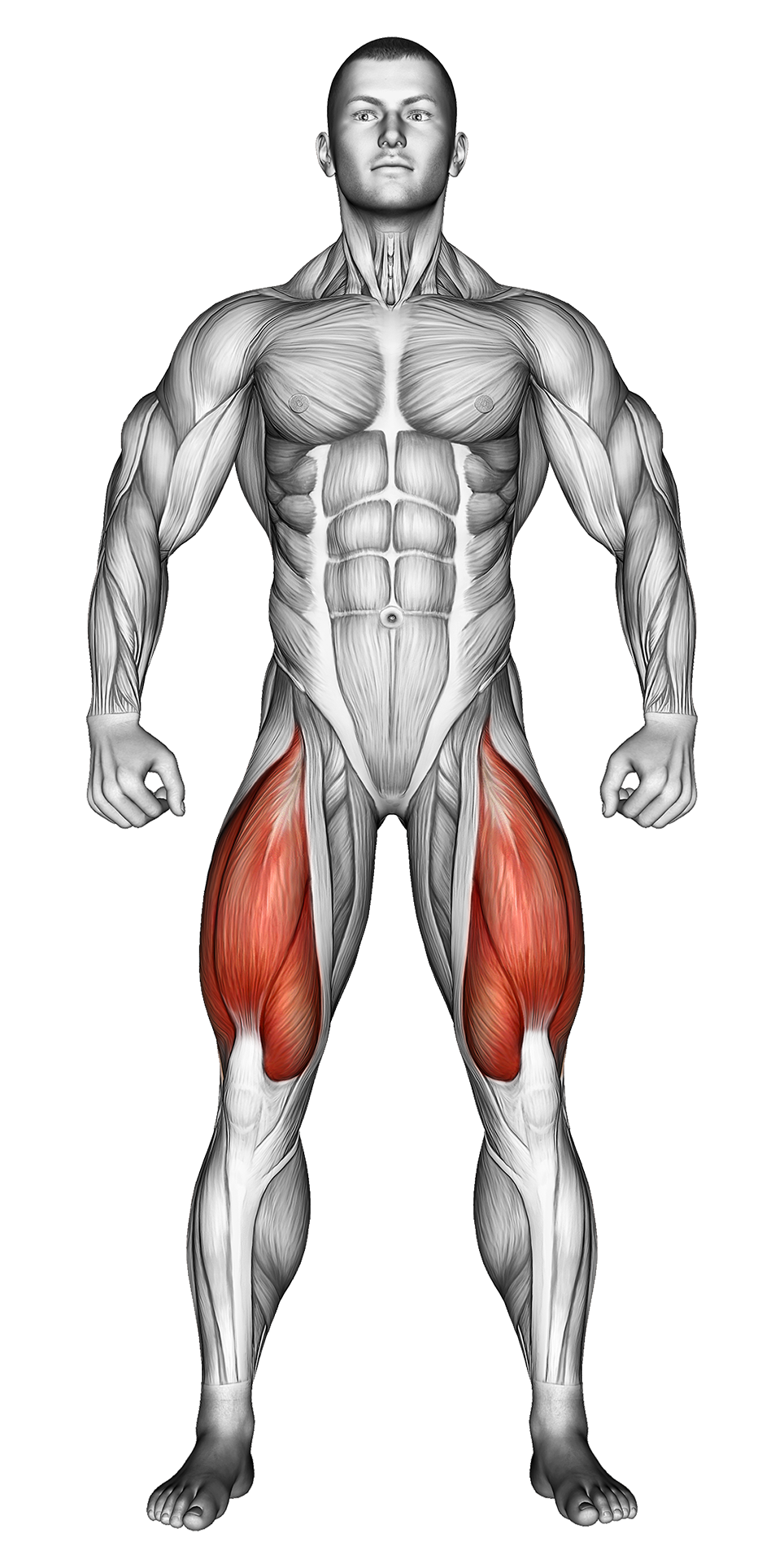
| Primary Muscle Group | Quads |
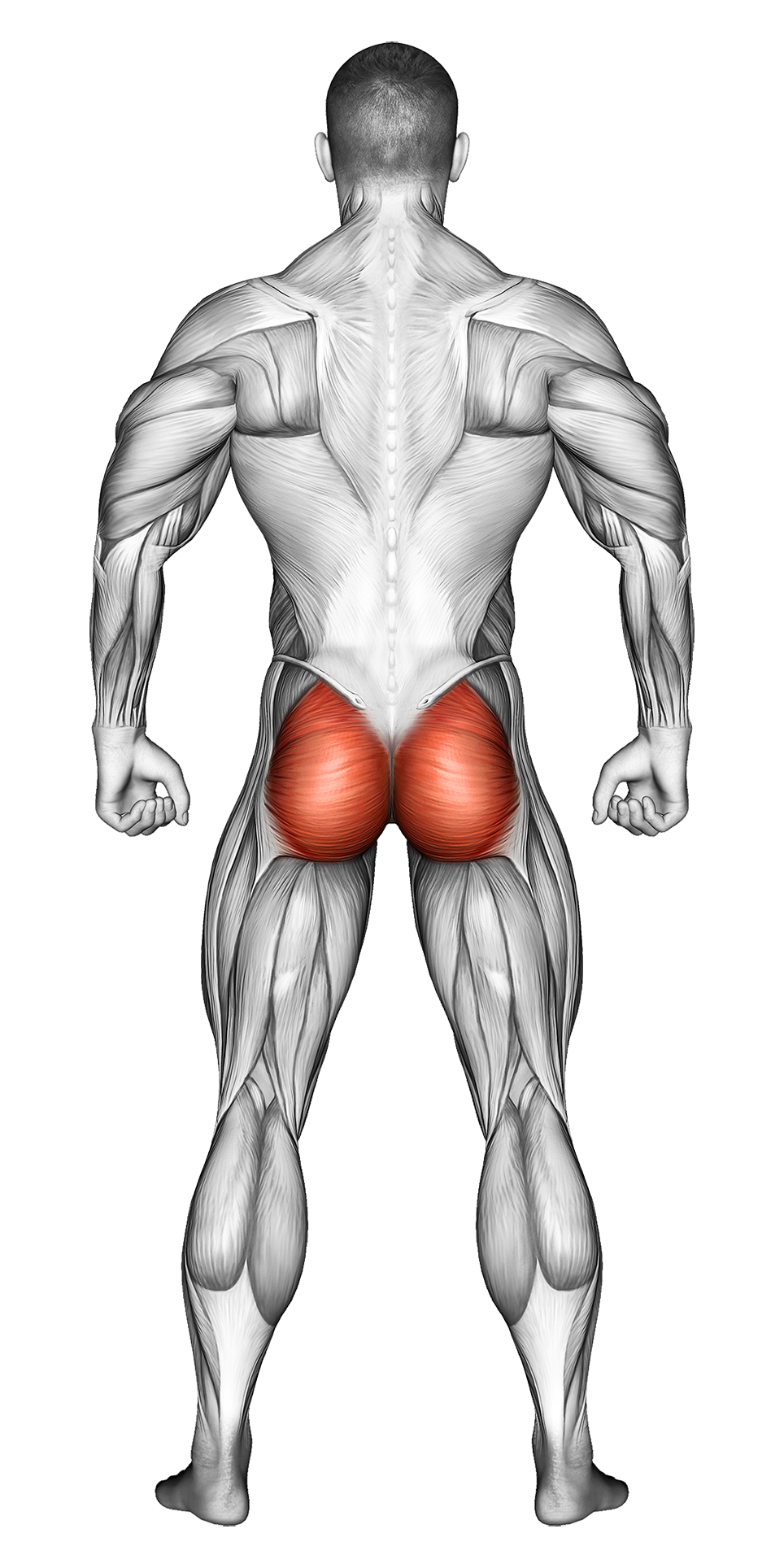
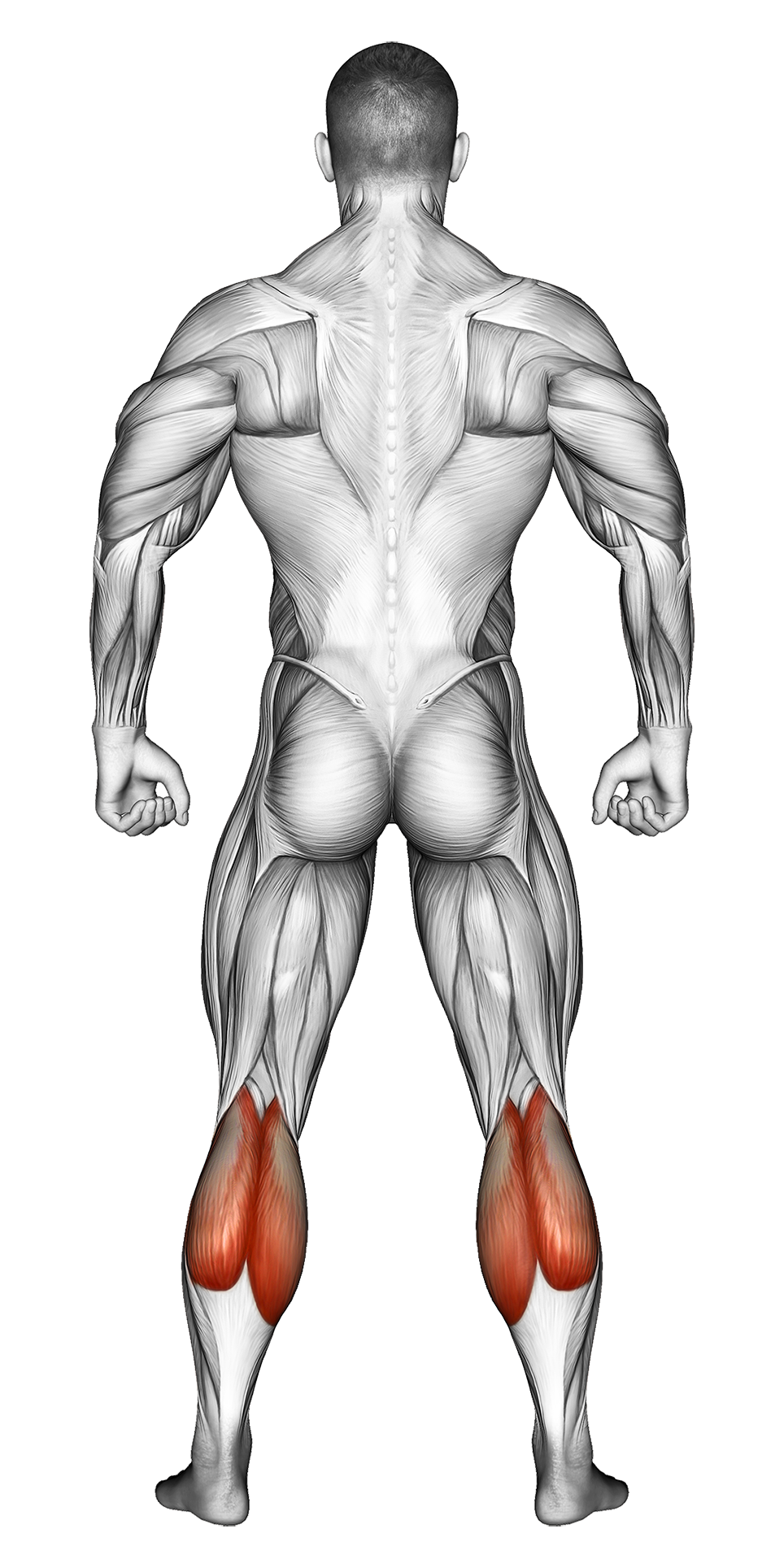
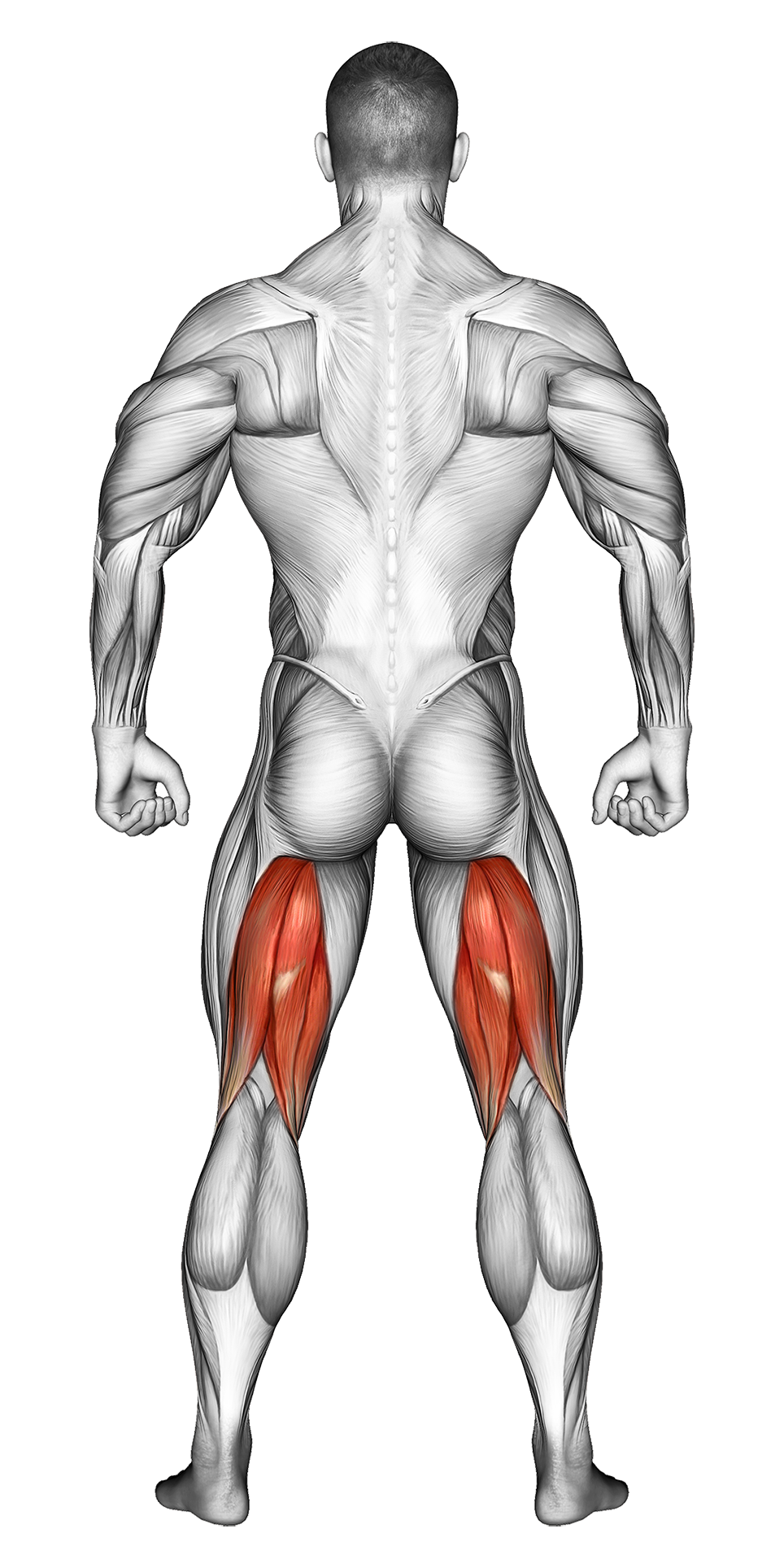
| Secondary Muscle Group | Glutes, Calves Hamstrings |
| Equipment Required | Kettlebell |
| Force Type | Push |
| Mechanics | Compound |
| Exercise Type | Strength |
| Difficulty | Intermediate |
Kettlebell Lunge: Video Tutorial & Exercise Guide
- 1.Kettlebell Lunge: Muscle Groups
- -1.1Primary Muscle Group
- -1.2Secondary Muscle Group
- 2.Kettlebell Lunge: Step-by-Step Guide
- 3.Kettlebell Lunge: Overview
- 4.Kettlebell Lunge: Benefits
- 5.Kettlebell Lunge: Pro Tips & Advanced Techniques
- 6.Kettlebell Lunge: Progression Plan
- 7.Kettlebell Lunge: Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Secondary Muscles Group
Kettlebell Lunge: Step-by-Step Guide
- Step 1: Stand tall with your feet hip-width apart, holding a kettlebell in each hand at your sides or with one kettlebell held in front of your chest in a goblet position.
- Step 2: Step forward with your right foot and begin lowering your body by bending both knees. Your right thigh should be parallel to the floor, and your left knee should hover just above the ground.
- Step 3: Make sure your right knee stays aligned with your toes and does not extend past them. Your weight should be evenly distributed between your front heel and the ball of your back foot.
- Step 4: Push through your right heel to return to the starting position, bringing your feet back together. Keep your torso upright and core engaged.
- Step 5: Repeat the movement with your left leg, alternating between legs for the desired number of reps.
Kettlebell Lunge: Overview
The Kettlebell Lunge is a lower-body exercise that targets the quadriceps, hamstrings, glutes, and calves. Holding kettlebells adds resistance and engages the core and grip muscles for increased overall stability and strength. This functional movement helps build leg power, balance, and coordination.
Whether holding a kettlebell in each hand or in a goblet position, Kettlebell Lunges are an effective way to improve unilateral leg strength, address muscle imbalances, and enhance lower body performance. They are also great for boosting flexibility and mobility in the hips and knees.
Kettlebell Lunges: Benefits
Kettlebell Lunges primarily target the quadriceps, hamstrings, and glutes, helping to build lower body strength and endurance. The added resistance of the kettlebells increases the intensity, making it an effective exercise for muscle growth and functional strength.
This movement also enhances balance and coordination, as each leg works independently during the exercise. The kettlebells also engage the core and upper body, making it a full-body movement that promotes stability and control.
Additionally, Kettlebell Lunges improve hip mobility and flexibility, which is essential for better movement patterns, injury prevention, and enhanced athletic performance.
Kettlebell Lunges: Pro Tips & Advanced Techniques
Keep your core engaged and your chest upright throughout the movement to avoid leaning forward. Focus on pushing through your front heel to engage your glutes and hamstrings. For an added challenge, hold the kettlebell in a goblet position or slow down the lowering phase (eccentric) to increase time under tension. Ready to build stronger legs and improve stability? Let’s lunge!
Kettlebell Lunges: Progression Plan
Beginner
Intermediate
Advanced
Kettlebell Lunge: Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What muscles do Kettlebell Lunges target?
+This exercise primarily targets the quadriceps, hamstrings, glutes, and calves, while also engaging the core and grip muscles for stability and control.
Are Kettlebell Lunges suitable for beginners?
+Yes, beginners can start with lighter kettlebells or bodyweight lunges to learn proper form and balance. Once you’re comfortable with the movement, gradually increase the weight for more resistance.
How can I make Kettlebell Lunges more challenging?
+To increase the difficulty, use heavier kettlebells or hold the kettlebell in a goblet or overhead position for added core and shoulder engagement. You can also slow down the movement or perform walking kettlebell lunges for increased intensity.
How often should I include Kettlebell Lunges in my routine?
+Include this exercise 2-3 times per week as part of your lower body or full-body workout. It pairs well with other functional movements like squats and deadlifts for a comprehensive lower body routine.
What common mistakes should I avoid?
+Avoid letting your front knee extend past your toes or allowing your chest to lean forward. Focus on keeping your torso upright, your core engaged, and your knees aligned with your toes throughout the movement.
Share
Don’t Wish for It, Work for It – Join the FlexXP Newsletter Today!
Thank you for signing up for the FlexXP Newsletter!
This site is protected and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.